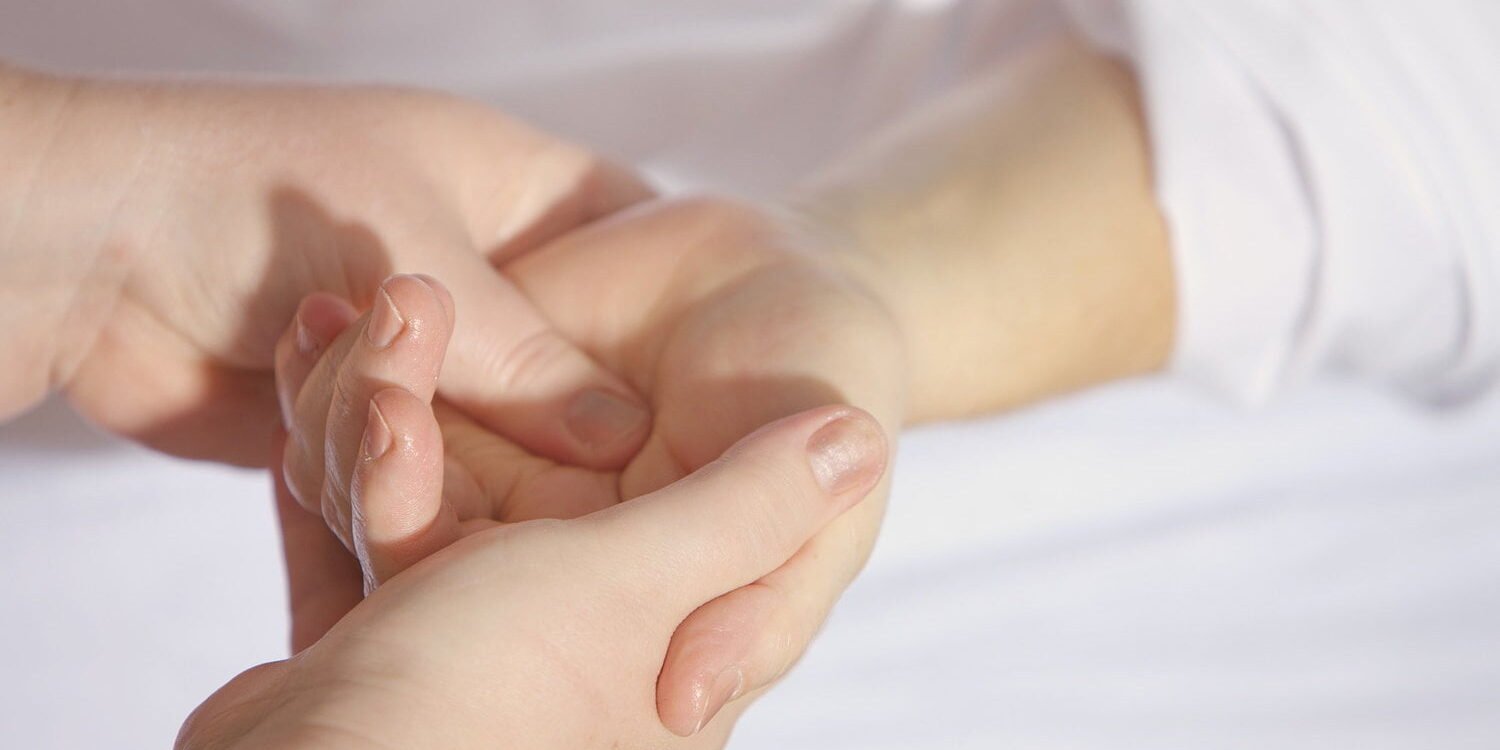
Many people around the world including Wake Forest, North Carolina sufers from Carpal tunnel syndrome. Many people like alternative treatment for this problem. Some clients like to learn about benefits of massage for carpal tunnel syndrome.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
Anatomy:
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist. It is bounded by bones on the bottom and sides and a ligament on top. Through this tunnel run the median nerve and the tendons that bend the fingers.
Pathophysiology:
CTS occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. This compression can result from swelling or any cause that decreases the size of the carpal tunnel or increases the size of the contents running through it.
Symptoms:
Numbness, tingling, or pain in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers.
Symptoms often occur at night because many people sleep with flexed wrists.
A feeling of hand weakness or dropping things.
Symptoms might be exacerbated after activities that involve wrist flexion or gripping.
In prolonged cases, there can be muscle wasting at the base of the thumb.
Risk Factors:
Repetitive hand movements.
Wrist injuries.
Pregnancy (due to fluid retention).
Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and hypothyroidism.
Anatomical factors, like a naturally narrow carpal tunnel.
Frequent use of vibrating hand tools.
Diagnosis:
Clinical Examination: Checking for numbness, Tinel’s sign (tapping on the median nerve produces tingling), and Phalen’s test (forced wrist flexion produces symptoms).
Electrodiagnostic Testing: Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) tests can help confirm the diagnosis and determine its severity.
Imaging: In certain cases, MRI or ultrasound may be used, though they’re not typically first-line diagnostic tools.
Treatment:
Conservative Treatments:
- Wrist splinting, especially at night.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Activity modifications to avoid exacerbating activities.
- Physical therapy.
- Ergonomic modifications in the workplace.
Steroid Injections: Injecting corticosteroids into the carpal tunnel can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Surgery: Carpal tunnel release surgery might be recommended for severe cases or when conservative measures fail. The surgery involves cutting the ligament around the wrist to alleviate pressure on the median nerve.
Alternative Therapies: Some people benefit from yoga, chiropractic care, or acupuncture, though evidence is still emerging.
Prevention:
Regular breaks from repetitive tasks.
Ensuring ergonomic hand and wrist postures.
Stretching and strengthening exercises for the hand and wrist.
Prognosis:
With appropriate treatment, many people experience relief from symptoms. However, in prolonged cases where nerve damage is severe, complete recovery might not be possible.
If you or someone you know suspects they have CTS, it’s essential to see a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Massage for carpal tunnel syndrome
Massage therapy can be a complementary treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS). It may help to alleviate some of the symptoms by addressing the soft tissue components contributing to median nerve compression. Here’s a guide on how massage can be used to help with CTS:
Benefits of Massage for CTS:
Relief from Muscle Tension: Massage can relax tight forearm and wrist muscles that might be contributing to compression.
Improved Blood Flow: This can enhance the healing process by increasing oxygen and nutrient delivery to affected areas.
Reduction in Inflammation: Certain massage techniques might assist in reducing localized inflammation.
Release of Scar Tissue: If injury or chronic inflammation has resulted in scar tissue formation, massage might help break this down.
Techniques for CTS Massage:
Myofascial Release: This involves gentle sustained pressure on the myofascial connective tissue restrictions. The therapist will locate areas that feel stiff and immobile and apply pressure to release these areas, aiming to restore movement and reduce pain.
Deep Tissue Massage: This can be used on the forearm and wrist muscles to release chronic muscle tension.
Trigger Point Therapy: Applying direct pressure to specific points (trigger points) can help alleviate pain and tension.
Neuromuscular Therapy: This technique combines deep tissue work with trigger point therapy, focusing on the relationship between the nervous system and muscles.
Lymphatic Drainage: Gentle technique that can help reduce swelling in the carpal tunnel, which can alleviate pressure on the median nerve.
Steps for a Basic CTS Massage:
Start with a warm-up, using gentle effleurage (gliding) strokes on the forearm and hand.
Progress to deeper strokes, working specifically on the flexor muscles of the forearm.
Use thumb and finger pressure to apply localized deep pressure to tight or tender spots in the forearm muscles.
Massage the palm, focusing on areas that feel tense.
Finish with gentle stretching of the wrist and fingers.
Points to Note:
Always ensure that the pressure is comfortable for the recipient. Pain or excessive pressure can exacerbate symptoms.
It’s essential to differentiate between soreness that can sometimes occur after a deep tissue massage and the pain or numbness characteristic of CTS. If symptoms worsen after the massage, it might be necessary to adjust the techniques or pressure used.
Before starting any massage regimen, it’s essential to get a clear diagnosis from a healthcare professional to ensure that massage is an appropriate intervention for your specific case.
Lastly, while massage can be a useful adjunct therapy for CTS, it might not address the root cause, especially if there are structural issues or underlying medical conditions contributing to the syndrome. It’s essential to consider a holistic approach that may include ergonomic adjustments, physical therapy, and other interventions.